The Complete Law Firm SEO Glossary
These are the SEO terms that lawyers should know. We break them down into plain English that’s easy to understand.
A
Active Voice
A sentence where the subject does the action. For example, ”The cat chased the mouse.” Active voice is clearer and more direct than passive voice (”The mouse was chased by the cat.”). Always use active voice in your SEO. Less than 10% of your sentences should be in passive voice.
AdSense
A Google program that allows website owners to make money by showing ads on their website. It matches ads to your website based on your content and visitors.
AdWords (now called Google Ads)
A Google platform that lets businesses advertise online by placing ads in Google search results or on websites. It’s highly customizable and lets you put your ads in front of people looking for your products or services. Google Ads are good for getting immediate visibility and fast results.
Ahrefs
A paid SEO data tracking software with tools for link building, keyword research, competitor analysis, website health, search rankings, and other SEO metrics.
AI (Artificial Intelligence)
Machines or computer systems designed to think and learn like humans. Examples include chatbots, digital assistants, and recommendation systems.
Algorithms
A set of rules or instructions that computers follow to perform tasks like sorting data or showing search results.
Alt Text
A description added to images on a website so Google and visually impaired users can understand the image. Adding alt text optimizes images for SEO and helps Google rankings.
Analytics
Collecting and analyzing data to understand website traffic, user behavior, and other SEO metrics.
Anchor Text
The clickable text in a link. The anchor text should use keywords and tell you what the link is about.
Authority
Measures the credibility and trustworthiness of your website, according to Google. Authority is based heavily on the quality and number of links to your website.
Auto-fill (autocomplete)
The suggestions Google makes when you type in a search. The auto-fills are based on what other people searched for – they are the most popular searches on the topic. Thus, auto-fills can be great sources of keywords and key phrases for your SEO.
A/B Testing
Trying two different versions of something (like a web page or an ad) to see which works better.
B
Backend SEO
SEO settings that help your website rank higher on Google. Backend SEO includes site speed, coding, structure, metadata, URLs, Google snippets, and other technical components.
Backlinks (inbound links)
Links from other websites that point to your website. Backlinks boost your site’s authority and improve visibility in search results.
Black Hat
Unethical SEO tactics that break Google’s rules. Black hat tactics may work short-term but can get your website penalized or banned by Google. We don’t recommend using black hat techniques under any circumstances. The risk does not outweigh the reward.
Body Text
The text that forms the main content of a web page. The body text is typically in paragraph form and does not include the headings, images, charts, or other components of the web page.
Bounce Rate
The percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate usually means people didn’t find what they wanted. High bounce rates lead to lower rankings.
Branded Keywords
A keyword or search term that includes a brand name or product name. For example, ‘’Nike Shoes’’ instead of just ‘’shoes.’’
Broken Links
Links that don’t work because the web page was deleted or moved. Having broken links on your website causes it to rank lower in Google search results.
C
Caching
Storing a version of your website so it loads faster the next time someone visits. If you make changes to your website, you may have to clear the cache before the changes appear.
Call to Action
Words that tell people what to do, such as ‘’Buy Now’’ or ‘’Contact Us.’’ The call to action is how your website converts readers into clients. Every page on your website should have a call to action.
Cannibalization
Duplicating content from other pages on your website. Duplicate content causes your website to rank lower in Google search results. Cannibalization is like plagiarism; except you’re stealing content from your website instead of someone else’s.
Carousel
A slideshow of images that the viewer can click or swipe through.
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
The percentage of people who see your link and actually click it. Ads and web pages with higher click-through rates rank higher on Google.
Clicks
The number of times people click on your link. Clicks are a key metric for measuring the performance of ads and web pages.
Competitor Research
Checking what your competitors are doing to learn from them. Competitor research involves checking their keyword rankings, backlinks, domain authority, and other SEO metrics.
Content Marketing
Creating blogs, videos, and social media posts to attract customers. Good content marketing means your content is valuable, relevant, and consistent.
Content Strategy
A plan for what kind of content to create and how to use it to grow your business. Content strategy involves keyword research, competitor research, market research, and content scheduling.
Conversions
When a visitor to your website does what you want, such as signing up for your email list, filling out a contact form, calling you, buying something, or contacting you. A conversion is when a visitor becomes a lead (potential client).
Conversion Rate
The percentage of visitors who ‘’convert’’ (call, email, fill out a form, etc.).
Core Web Vitals
Google’s way of measuring how fast and easy to use your website is. Check your website’s core web vitals at PageSpeed Insights.
Crawl Depth
The number of clicks it takes to navigate from your home page to a particular page on your website.
CRM (Client Relationship Management)
Software that helps businesses keep track of customers and interactions. You can use CRMs for data tracking, sales, customer support, case management, marketing automation, and more.
Crowd Sourcing
Getting ideas, content, or services from the public (or a large group of people) online. Examples of crowd-sourced platforms include Wikipedia and Google Maps.
CSS
Code that controls a website’s colors, font, layout, and other design features. CSS makes the website look good and creates a user-friendly experience.
D
DNS (Domain Name System)
The system that translates human-readable website names (like signaigolegalcontent.com) into machine-readable IP addresses (like 196.0.8.47) so computers can find them.
Dofollow link
A normal link that tells Google to count it. Dofollow links to your website increase its domain authority and boost rankings. Dofollow links are different from nofollow links, which don’t impact domain authority or Google rankings.
Domain
The name of a website (like signaigolegalcontent.com).
Domain Authority
A score that measures how well a website ranks on Google. The number and quality of backlinks to the site heavily influence domain authority.
Duplicate Content
Content that appears in more than one place. Google scores for originality, so duplicate content causes your website to rank lower.
E
E-E-A-T
An acronym that stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness – the factors that Google uses to judge content quality. Higher levels of E-E-A-T mean higher Google rankings.
Email Capture
Collecting email addresses from website visitors so you can send them marketing emails later. Email capture is often facilitated by a lead magnet – a high-value piece of content you give away for free in exchange for an email address.
Engagement
A measure of how much people interact with your content (likes, comments, shares, reactions, etc.). Content with higher levels of engagement ranks higher in search engines and social media feeds.
Evergreen Content
Content that stays relevant and continues driving traffic to your website for a long time.
External Link
A link that takes you to a different website. Make sure the external links on your website open in a new tab. Otherwise, when someone clicks the link, Google will count it as leaving your website – negatively impacting rankings.
F
Featured Snippet
Special Google search results where the format is reversed – showing the description of the article above the article’s title.
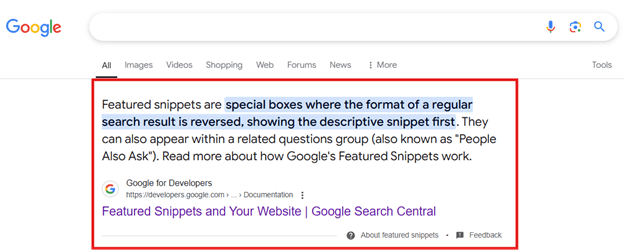
(Example of a Featured Snippet)
G
Gap Analysis
Identifying which keywords your competitors are ranking for that you are not. Gap analysis pinpoints missing content pieces.
Google Ads
Google‘s paid advertising platform. It is highly customizable and offers many different types of ads – including search, display, shopping, video, app, performance max, local, and more.
Google Analytics
A free tool that tracks how people use your website. It is one of the most important data tracking tools because you get feedback directly from Google.
Google My Business (GMB)
A free tool to manage your business info on Google. Completing your GMB profile is 100% necessary for your SEO. Make sure to claim your GMB profile and complete it if you have not done so already.
Google Reviews
Customer reviews that show up in Google search results. Google reviews are crucial for your SEO. The more 5-star reviews you have, the more relevant you are in search results. 5-star reviews and testimonials are the best evidence that you are great at your work.
Google Search Console
A free tool that lets you track your website’s search performance. Google Search Console is one of the most important SEO tools because it allows you to communicate directly with Google. Google Search Console is essential for identifying and troubleshooting problems with your website.
Google Snippet
A short preview of a webpage in Google search results. It includes the title and a short description, and may include other features.
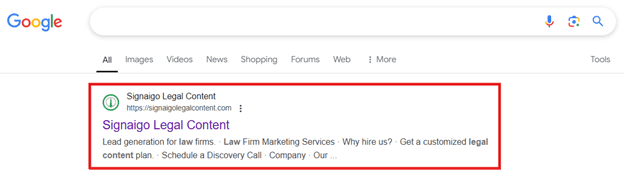
(Example of a Google Snippet)
GPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer)
A type of AI (such as ChatGPT) that generates text, images, and other types of content.
Gray Hat
SEO tactics that are not quite against Google‘s rules but are not fully safe either. Gray hat SEO techniques are not best practices, and we advise against using them. Gray hat techniques can lead to penalties, bans, and other negative consequences.
Guest Blogging
Writing an article for another website to get exposure and backlinks. We suggest guest blogging on related, high-ranking websites to boost your SEO.
H
Header Tags
Formatting tags (H1, H2, H3) used to structure your web page (see Headings).
Headings
Titles and subtitles that organize content on a web page. Formatting your headings properly (H1, H2, H3) is crucial for your SEO. Google uses your headings to understand the intent and purpose of the article and properly categorize it. We suggest using keywords, related keywords, and local keywords in your headings.
Use headings for every paragraph or two of your articles (maybe three if the paragraphs are short). Using lots of headings makes your article easy to read and scan, leading to lower bounce rates. Do not underestimate the importance of headings for your SEO.
Hosting
The service that stores your website and makes it available online. Popular hosting providers include GoDaddy, Hostinger, Bluehost, WordPress, and others.
HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language)
The code that websites are built with. HTML is the most basic building block of a website.
HTTP Response Codes
Numbers that show if a webpage loads properly (for example, 404 is a type of error that means ‘’not found.’’)
I
ICP (Ideal Client Profile)
A description of the perfect client for your business. It includes demographic information, needs, pain points, and behavior patterns.
Index
The entire database of web pages that Google stores and shows in search results. It’s similar to a library index, which lists information about all of the books in the library. When you add new pages to your website or update existing pages, it’s important to have Google index them. You submit index requests using Google Search Console.
Image Compression
Reducing the file size of images so a website loads faster.
Image File Size
The amount of space an image uses on a computer or memory card.
Impressions
The number of times your website appeared in Google search results. For social media, impressions are the number of times people viewed your content.
Indexing Errors (crawling errors)
Problems that stop Google from adding a page to search results (404 errors, blocked pages, server errors, broken links, etc.).
Integrity
The trustworthiness of a website and its content.
Internal Links
Links that connect pages within the same website. Every page on your website should contain at least one internal link. An extensive network of internal links boosts your SEO.
IP Address
A unique number that identifies a device on the internet.
J
Javascript
A computer programming language that makes websites interactive. It is a core programming language of the internet, along with HTML and CSS.
K
Key Phrases
Groups of words that people search for in Google (such as ‘’best personal injury lawyer in San Diego”). In other words, they’re multi-word search terms.
Keywords
Words that people type into Google to find what they’re looking for.
Keyword Density
How often a keyword appears in a piece of content. Keyword density is typically measured as a percentage. The ideal keyword density for SEO is 1-3% (1-3 words out of 100). You can quickly measure keyword density using a WordPress plugin like Rank Math or Yoast. If your keyword density is too high, use synonyms and related keywords instead. Synonyms and related keywords do not count towards keyword density.
Keyword Difficulty
An SEO metric that measures how hard it is to rank for a keyword. The higher the keyword difficulty, the harder it is to rank for the keyword on Google due to high competition. Keywords in the legal industry are the most competitive and difficult to rank for of any industry.
Keyword Ranking
A website’s position in search results for a particular keyword.
Keyword Research
Finding the best keywords to target. Keyword research involves identifying the most relevant keywords and doing competitor analysis.
Keyword Stuffing
Overusing keywords in a spammy way. Keyword stuffing causes your keyword density to be too high. Google penalizes keyword stuffing.
KPI (Key Performance Indicator)
A metric that shows if something is successful. KPIs for SEO include traffic, conversions, keyword rankings, domain authority, click-through rate, and others.
L
Landing Page
A webpage designed to convert visitors into clients. When you run Google Ads, each ad should have a landing page. You should optimize every landing page for speed and mobile functionality and include a clear call to action.
Lead
A lead is a potential client who has shown interest in your law firm by contacting you or engaging with your content. Viewers convert to leads by signing up for your email list, filling out a contact form, calling you, emailing you, direct messaging you, buying something, or contacting you by other means.
Lead Generation
Attracting potential clients. Lead generation techniques include SEO, pay-per-click, web design, social media, in-person networking, and more.
Lead Magnet
A high-value piece of content you give away for free in exchange for an email address. Lead magnets are key for building your email list. Your lead magnet should solve a major problem for your ideal client.
Lead Nurturing
Keeping in touch with leads until they are ready to buy. Your email newsletter is a key tool for lead nurturing.
Links
Clickable connections between two pages on the internet. Links include internal links (links to pages on the same website) and external links (links to other websites). Internal and external links are essential to your SEO.
Link Building
Getting other websites to link to your website. Link-building techniques include creating profiles on attorney directories and business directories, creating profiles on social media, doing interviews and podcasts, posting job opportunities on job websites, guest blogging, hosting events, and more.
Link Stuffing
Cramming as many links as possible into an article in a spammy way. Google penalizes link stuffing – it harms your SEO. Every link should be on-topic and add something to the article. Use links often, but only when it makes logical sense.
LLM (large language model)
An AI system (like ChatGPT) that processes and generates text, images, and other types of content.
Loading Time
How long a webpage takes to load. Slow loading times cause people to leave your website, resulting in a higher bounce rate and lower Google rankings.
Local Map Pack
The map and business listings that appear in local Google search results. The local map pack includes the business’ contact info, address, reviews, website link, hours of operation, photos, pricing, and more.
Location Keywords
Search terms that include a place (such as ‘’immigration lawyer in San Diego’’).
Long-Tail Keywords
Specific search phrases that contain several words (such as ”San Diego bicycle helmet laws”). It’s easier to rank for long-tail keywords than for more general ones (like ”helmet laws”). We suggest using long-tail keywords in high-competition markets where ranking is hard.
LSA (Local Service Ads)
Paid ads that show up for local businesses in Google. LSAs are geographically based.
LSM (Local Search Marketing)
Marketing that focuses on getting local clients. It involves optimizing your SEO for local search results. Local search marketing is especially important for lawyers because clients often need a lawyer in their area.
M
Metadata
Information about a webpage that helps search engines understand it. Metadata includes the page’s title, description, tags, keywords, and other data. Optimizing your metadata is necessary for good SEO.
Meta Description
A short summary of a web page that appears in search results. Meta descriptions differ from Google snippets because you control the meta descriptions you write for your website. You do not control the Google snippet. Google may use your meta description or create its own snippet from the content on your website.
The meta description convinces people to click on your link instead of a competitor’s. Thus, it should contain sharply written copy that makes readers want to read the article (no boring or generic text).
Meta Tags
Hidden tags in a webpage’s code that tell search engines what the page is about. You can use a WordPress plugin like Rank Math or Yoast to add meta tags to your web pages.
Mobile Functionality
How well a website works on phones and tablets. Good mobile functionality is essential for your SEO. Up to 80% of your traffic may be coming through mobile devices. Prioritize the mobile experience on your website – think ”mobile first.”
You can check your website’s mobile functionality score at PageSpeed Insights. Google rewards mobile-friendly sites with higher rankings. Your SEO will suffer if your website has poor mobile functionality.
Moz
A software company that provides SEO tools and resources for keyword research, rank tracking, backlink analysis, and more.
N
NAP (name, address, phone number)
Key business information that should always be consistent across the internet. Any time these details change, update them on your Google My Business profile, social media profiles, attorney directory, business directory profiles, and anywhere else they appear online.
Newsletter
Emails sent regularly to subscribers. Newsletters typically contain updates, promotions, and valuable content. Your newsletter should always be of high value to the reader.
Nofollow
A tag that tells Google not to count a link for domain authority or rankings. Nofollow links are different from Dofollow links – which are normal links that count towards a site’s ranking power.
Noindex
A tag that tells Google not to index a page in search results. Noindex tags may be used for ”thank you” pages, ad landing pages, privacy policy pages, and other pages not intended to be optimized for SEO.
O
Off-Page SEO
SEO techniques that take place off of your website. Off-page SEO includes link building, social media, guest blogging, podcast appearances, and more.
One-Way Links
Links from one website to another without a return link. One-way links are not reciprocal. Google values one-way links higher than reciprocal links for rankings.
On-Page SEO
SEO techniques that are visible to the reader (such as keywords, headings, and links).
Organic Search Results
Free Google search results (not paid ads).
Originality
Unique content that isn’t copied from other sources. Google scores for originality. Original content ranks higher than duplicate content.
Outbound Links (External Links)
Links that take users to a different website.
P
PageRank
Google‘s system for ranking websites. PageRank is highly influenced by the quality and number of backlinks pointing to your website. Other factors impacting PageRank include content quality, technical SEO, keyword optimization, speed and mobile functionality, metadata, and more.
Page Speed
How fast a webpage loads and performs. You can check your website’s Page Speed at PageSpeed Insights.
Pages per Session
The number of pages a viewer visits before leaving your website. Higher pages per session typically mean better user engagement, lower bounce rate, and higher rankings. Content that is engaging, relevant, and easy to navigate leads to higher pages per session.
Page Title
The main title of a webpage that appears in search results. Optimizing the Page Title is essential for SEO. The Page Title should be tagged as H1 and should include keywords. The Page Title is often called the Title Tag.
Page Views
The number of times a web page is visited. Page views are a key metric for measuring website traffic.
Pagination
Splitting up long content into a multi-page list. For example, if your website’s blog contains many articles, it may span several pages (Page 1, 2, 3, etc.).
Paid Search
A marketing tactic where businesses pay search engines like Google to appear at the top of search results. Pay-per-click (PPC) is a type of paid search where the business pays the search engine each time a user clicks on their ad.
Passive Voice
An indirect sentence structure where the subject receives the verb’s action (for example, ”Fred was hit by John” instead of ”John hit Fred”). SEO should be in active voice rather than passive voice. Active voice is easier to read and understand.
Avoid Passive Voice in your writing. Less than 10% of your sentences should be in Passive Voice. You can use grammar-checking software like Grammarly to identify and eliminate Passive Voice from your SEO.
Penalty
Penalties are punishments for breaking Google’s rules. Google penalizes unethical conduct and behavior that goes against its community guidelines. Penalties include lower rankings and even being completely removed from search results. Google penalties are also called ‘’manual actions.’’
Pillar Content
Content that covers a main topic in-depth with links to related posts. For attorneys, your Practice Area Pages are your Pillar Content.
Plagiarism
Copying someone else’s content without permission. Plagiarism harms your website’s rankings and may result in penalties from Google. Do not plagiarize. We suggest using plagiarism-checking software like Grammarly to remove duplicative language before publishing SEO.
Pmax (Performance Max)
An automated Google Ads campaign type that uses AI to optimize your ads. Pmax campaigns can show ads across all of Google’s platforms: Search, Display, Maps, Gmail, YouTube, Shopping, and more.
Popularity
The amount of traffic that visits your website. Google ranks websites based on popularity, relevancy, and integrity. The number and quality of backlinks that point to your website greatly influence your website’s popularity.
PPC (Pay Per Click)
Ads where businesses pay every time someone clicks on their ad. PPC costs in the legal industry are the highest of any industry due to high competition. PPC is good for generating immediate traffic but is an ongoing cost. Check our PPC vs. SEO article for a complete discussion of the costs and benefits.
Practice Area Pages
Webpages dedicated to the types of cases you handle. For attorneys, Practice Area Pages are your Pillar Content. Practice Area Pages should be at least 2,500-5,000 words. They should go into deep detail and answer every possible client question about the topic. Each of your sub-practice areas should have its own Practice Area Page. Your Practice Area Pages should include your successful case results within that area.
Primary Keyword
The main keyword or key phrase a webpage targets (such as ”car accident lawyer”). It’s the main search term that your page is trying to rank for.
Q
Quality Content
Content that is useful, well-written, engaging, well-organized, and properly formatted.
Query
The words people type into a search engine to find what they are looking for.
R
Rankings
The position where a webpage appears in Google search results. The primary factors influencing a website’s rankings are its relevancy, popularity, and integrity.
Readability Score
A measure of how easy a website is to read. You can check an article’s readability score with Microsoft Word or a writing assistant like Grammarly.
Reciprocal Links (Two-Way Links)
When two sites link to each other. Google values one-way links more than reciprocal links for rankings. ”Link trading” is frowned upon.
Redirect
When one URL sends visitors to another URL instead. Redirects tell visitors and Google that a webpage has a new location.
Related Keywords (Secondary Keywords)
Similar words or phrases related to the main keyword, including synonyms. Related keywords do not count towards an article’s keyword density.
Relevancy
How well a webpage matches the searcher’s intent for a specific keyword or key phrase. Factors influencing relevancy include keyword density, backlinks, keywords in the anchor text of links, and time spent on the page. The more time viewers spend on the page, the more relevant the page is to the viewer’s search terms.
Rich Snippets
Google search results with extra details like star ratings, pricing, and images.
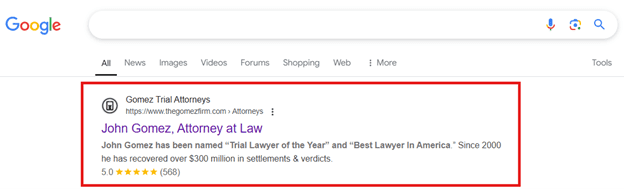
(Example of a Rich Snippet)
ROI (Return on Investment)
The profit made from an SEO or marketing campaign. It is essential to continuously track your SEO and ad data to maximize ROI. Allocate more resources to what is working and adjust what is not.
S
Sales Funnel
The steps people take before buying something online. Tracking user behavior at each sales funnel stage is how you optimize the process and improve ROI.
Schema
Code that helps Google understand what’s on a webpage.
Scraping
Collecting data from websites.
SearchGPT
AI technology that is used for searching and answering questions.
Search Volume
How often people search for a keyword. Keywords with higher search volume are typically more difficult to rank for and more expensive to purchase ads for.
SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
Paid and unpaid strategies to get more website traffic and generate business online.
Semrush
A popular SEO tool with features for keyword research, competitor analysis, backlink analysis, ad optimization, and more.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
The process of improving a website to rank higher on Google. Many factors influence SEO, including content quality, backlinks, website design, schema, speed and mobile functionality, website integrity, and more.
SEO Audit
A review or checkup of your website to see if it’s working well. An SEO audit includes keyword analysis, backlink analysis, competitor research, rankings research, page speed and mobile functionality, and other SEO metrics.
SERP (Search Engine Results Page)
The page of results you see after typing something into Google. SERPs show both organic search results and paid ads.
Sessions
A visit to a website, including all pages viewed during the visit.
Session Duration
How long someone stays on a website before leaving. Higher session durations mean users spend more time engaging with your content, leading to higher rankings and conversion rates.
Short-Tail Keywords
Simple, broad keywords (like ”lawyer”). Competition for short-tail keywords is typically higher, making them more difficult to rank than long-tail keywords.
Sitelinks
Extra links that appear under a search result to help users navigate a site. They are shortcuts that allow users to find the information they are looking for quickly.
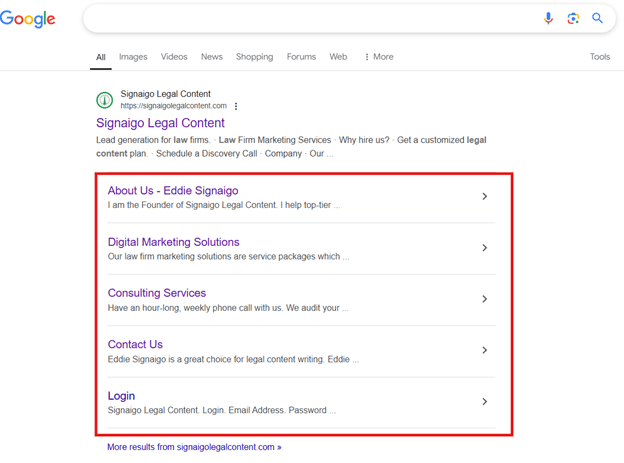
(Examples of Sitelinks)
Sitemap
A list of all the pages on your website. Sitemaps help search engines find and index all of your website’s content.
Spam
Unwanted, low-quality content meant to trick search engines. Spam content harms your website and results in lower rankings. Google penalizes spammy content and links.
Spam Backlinks
Low-quality links that can hurt SEO. You remove spam backlinks by disavowing them in Google Search Console.
Spider (Crawler)
A bot that scans websites for Google. They gather and store data, such as the content and quality of the website.
Social Media
Platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter where people and businesses publish content. Social media profiles influence your SEO by providing backlinks, relevant search results, and free advertisement. Claiming your law firm’s name on all social media platforms prevents others from stealing it.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)
A security feature that encrypts website data. It provides privacy, authentication, and integrity.
Subdomain
A website section with its own web address (like blog.example.com). Subdomains help you organize your content and business offerings.
T
Tags
Keywords or labels used to organize content. Title tags and header tags are essential to your SEO. They help Google understand and categorize your content.
Technical SEO
The behind-the-scenes fixes that make a website run smoothly. Technical SEO includes optimizing images, caching, crawling and indexing, site mapping, SSL certificates, schema, fixing broken links and redirects, optimizing URL structure, and more.
Testimonial
A customer review that builds trust. Testimonials are the most powerful evidence that you are great at your work. Put testimonials on every page of your website in visible places. The best place for a testimonial is right next to the claim that it supports. Testimonials and 5-star reviews on your Google My Business page are especially important because they greatly impact your search rankings.
Title Tag
The title that appears in search results (see Page Title).
Time on Page
How long a visitor stays on one page. Higher time on page means visitors spend more time engaging with the content, leading to higher rankings and conversion rates.
Traffic
The number of people who visit your website. Traffic is a primary metric that measures your SEO performance.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
An extra security step to protect your accounts. Use 2FA to access your website and hosting accounts to prevent hacks.
U
UI/UX (User Interface/User Experience)
How a website looks and how easy it is to use. Good UI/UX means the website is fast, easy to use, well-organized, visually appealing, and mobile-friendly. Websites with poor UI/UX rank lower on Google.
Unique Content
Content that has not been copied from somewhere else and doesn’t appear anywhere else on the internet. Unique content ranks higher on Google. Google rewards originality and punishes duplicate content.
Unnatural Links
Links artificially created to manipulate Google rankings. Unnatural links violate Google’s rules and can result in penalties.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
The address of a webpage (like www.yourwebsite.com).
URL Structure
How a website’s URLs are organized. We suggest using ”https” in your URLs rather than ”http.” Whether you use ”www” in your URLs doesn’t matter, but choose whether you will use it or not and keep it consistent. Example: https://signaigolegalcontent.com.
User Intent
What a person is looking for when they type something into Google. The better your website satisfies the user’s intent, the more time they will spend on it, and the higher it will rank on Google.
USP (Unique Selling Point)
What makes your business different from the competition. Your USPs are the backbone of your messaging because they make you stand out from competitors.
V
Visitor
Someone who visits your website.
W
Web Server
Powerful computer systems that host websites and make them accessible on the internet.
White Hat
SEO techniques that follow Google’s rules and guidelines. White hat techniques improve your Google rankings while maintaining the integrity of your website. White hat techniques are the opposite of black hat techniques (which break Google‘s rules and result in penalties).
WordPress
A popular and highly customizable website-building platform. WordPress is the platform we use to build websites for our clients.
X
XML Sitemap
A file that helps Google find and index all of the pages on your website. It also helps Google understand your website structure. XML sitemaps help speed up content discovery.
#
301 Redirect
A permanent redirect from one URL to another.
302 Redirect
A temporary redirect from one URL to another.
404 Error
An error message that appears when someone tries to access a URL that no longer exists or cannot be found.
500 Error
A general ‘’catch-all’’ error message that indicates a problem with the web server.
Want help with your law firm SEO?
We offer a variety of products and services to help you generate business online.
SEO Course
This do-it-yourself option teaches you everything you need to know about SEO. The SEO Course is great for law firm owners, marketing departments, and marketing agencies with law firm clients. It includes videos, slides, an e-book, SEO checklists, a storytelling mini course, and more.
SEO Audit
Take the guesswork out of growing your firm online with our SEO Audit. It includes a 30-Minute Discovery Call, a detailed Audit Report, and a customized SEO Plan. The SEO Audit is great for law firms who want a clear path towards achieving their goals online.
Consulting
A done-with-you option where we help you solve your most difficult SEO challenges step-by-step. Our Consulting service includes an hour-long weekly phone call, website auditing, data tracking and analysis, 1-on-1 problem solving, weekly progress reviews, and a weekly action plan. Our Consulting service is a great option for firms that have marketing teams and want to boost their performance.
Solutions
SEO, PPC, and website design done for you. We build you a world-class website and handle all the updates and maintenance. Our Solutions package includes top-notch SEO, PPC ad management, a high-performance WordPress website, data tracking and analysis, phone and email support, proprietary APIs, and much more. We’re on it, so you don’t have to be.

